
REST vs. GraphQL: Key Differences and When to Use Each
Navigating the API landscape? This article meticulously dissects the core differences between REST and GraphQL, exploring architectural styles, data r...
Discover the latest insights, tutorials and expert analysis on cloud computing, serverless architecture and modern technology solutions.
Stay updated with the latest trends and insights in cloud computing technology

Navigating the API landscape? This article meticulously dissects the core differences between REST and GraphQL, exploring architectural styles, data r...

Optimize your serverless applications with the AWS Lambda Power Tuning tool, a valuable resource for navigating the complexities of function optimizat...
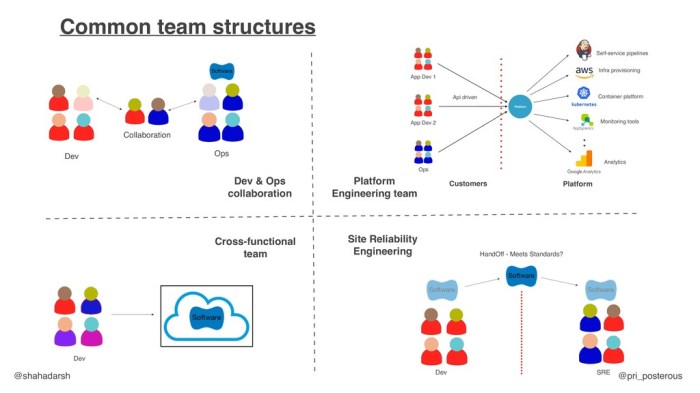
Platform engineering teams are vital in modern software development, providing the infrastructure and tools that streamline the entire development lif...
Discover how managed database services are transforming data management for businesses. This approach offers significant advantages over self-managed...

Cloud architecture decisions are fundamental to an organization's success in the cloud. This article provides a comprehensive guide to effectively doc...

A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) serves as a central hub for all IT infrastructure data, essentially a digital blueprint of your organizatio...

This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of securing the Kubernetes control plane, covering essential aspects from authentication and aut...

This article delves into the crucial "Optimize" phase of the FinOps lifecycle, outlining strategies to proactively manage and reduce cloud costs. From...
This guide provides a detailed roadmap for developing a successful cloud-native database strategy. It covers crucial aspects like defining requirement...

Protecting sensitive data in cloud native applications requires robust secret management strategies. This guide outlines critical best practices for s...
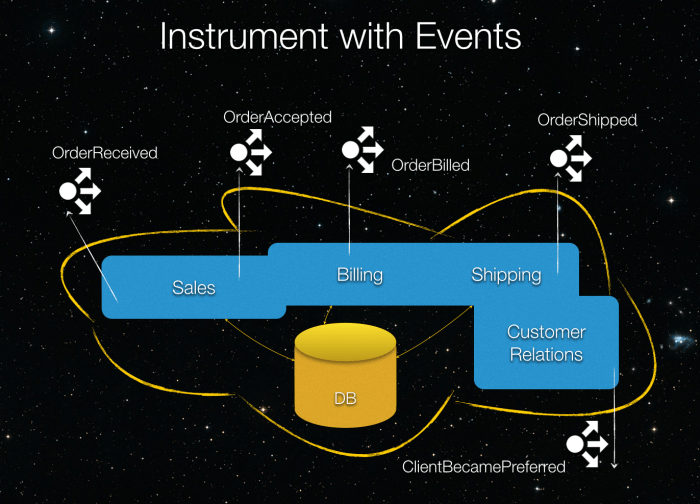
Struggling with a "Big Ball of Mud" (BBOM) architecture? This comprehensive guide provides a step-by-step approach to refactoring your unwieldy codeba...
This article provides a comprehensive guide to building a FinOps dashboard specifically tailored for executives, enabling data-driven cloud spending d...